Aortic And Peripheral Arterial
Embolism Or Thrombosis
Thromboembolism
Thromboembolism is a condition where a blood clot formed inside a blood vessel breaks loose and travels through the bloodstream, blocking a blood vessel in another organ, which can lead to organ damage. Affected organs may include the lungs (pulmonary embolism), brain (stroke), gastrointestinal tract, kidneys, or legs.
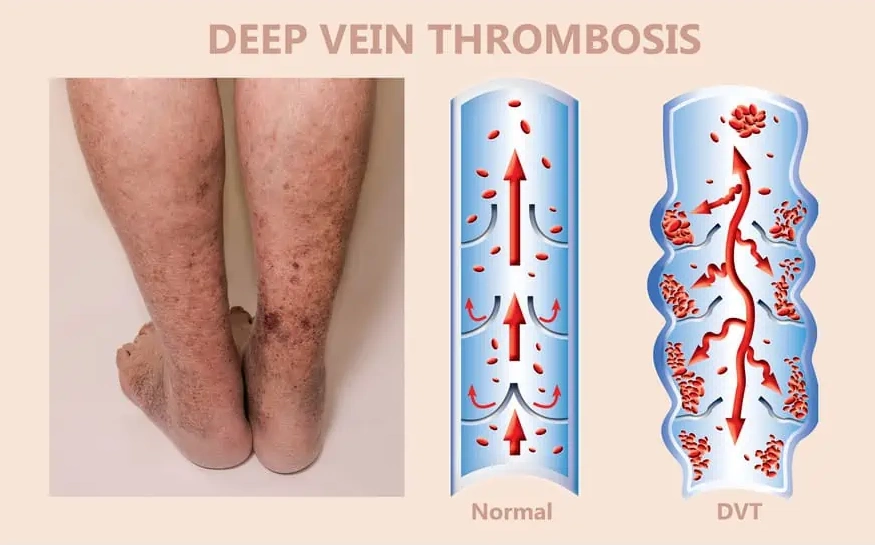
Two common diseases associated with thromboembolism are DVT (deep vein thrombosis), which involves a blood clot in a deep vein, and PE (pulmonary embolism). These conditions can develop as complications following cancer-related surgery.
Several risk factors for the development of thromboembolism in cancer patients have been identified, including the site and stage of cancer, the type of cancer, advanced disease, patient comorbidities, specific therapeutic agents, surgery, chemotherapy, and hospitalization.
Nearly 50 percent of patients with thromboembolism do not show any symptoms. Additionally, symptoms of thromboembolic diseases, such as DVT, may go unnoticed for a while since they are similar to those of various other health problems. Typical symptoms include swelling, tenderness, changes in skin color, and warmth over the affected area. If a blood clot breaks free and travels to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism, additional symptoms such as coughing up blood, sharp chest pain, and shortness of breath may also occur.
As a part of the diagnosis, your doctor will conduct a physical examination. He/she may ask questions related to your overall health and assess your medical history to exclude other causes. Your physician may also order tests specific to DVT such as a Duplex ultrasound, venography, and MRI.
Schedule an Appointment Today
If you or a loved one may benefit from treatment, book an appointment with us today!
Treatment for Thromboembolism
The aim of the treatment is three-fold and includes:
- Preventing the clot from getting bigger
- Preventing the clot from loosening and breakage
- Reducing the chances of DVT recurrence
Treatment options typically involve the use of blood-thinning medications, such as heparin and warfarin. In severe cases, clot-busting medications like tissue plasminogen activator (TPA) may be prescribed. Other treatment measures include inserting filters into veins to prevent clots from breaking loose and traveling to the lungs. Additionally, compression stockings may be worn to prevent blood from pooling and clotting.
Important Links
Practice Location
- © Dr. Neil Desai, Vascular Surgeon Cypress, Houston, TX

