Renal Vascular Disease
What is Renal Vascular Disease?
Renal vascular disease is a medical condition that affects the blood flow into and out of the kidneys. Kidney damage, kidney failure, and high blood pressure are all possible consequences of renal vascular disease.
What are the Types of Renal Vascular Disease?
The different types of renal vascular disease include:
What are the Causes of Renal Vascular Disease?
Some of the causes of renal vascular disease include:
- Atherosclerosis
- Injury
- Infection
- Surgery
- Tumor
- Aneurysm
- Pregnancy
- Certain medicines
- Birth defect
- Diabetes
- Hypertension
- Morbid obesity
- Fibromuscular dysplasia
- Underlying inflammatory disease
Some of the risk factors of renal vascular diseases include:
- Older age
- Being a woman
- Atherosclerosis
- Smoking
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
What are the Symptoms of Renal Vascular Disease?
The symptoms of the renal vascular disease vary depending on the type of disease and the extent to which it has affected the body. The following are some common symptoms of renal vascular disease:
- High blood pressure
- Increased urea in the blood
- Blood in the urine
- Nausea and vomiting
- Skin lesions or reddish discoloration of the skin
- Discolored areas of the toes and feet
- Fever
- Diarrhea
- Weight loss
- Muscle aches
- Kidney failure lesions or reddish discoloration of the skin
- Sudden onset of side pain or soreness between the ribs and the upper border of the hip bone
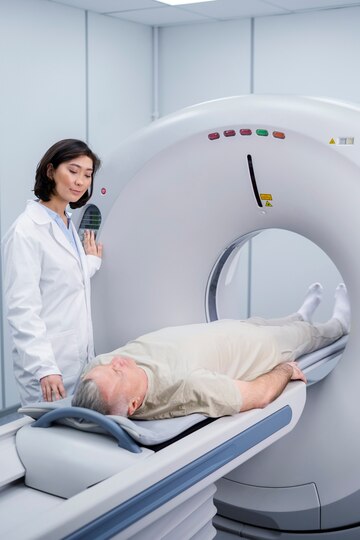
Diagnosis of Renal Vascular Disease
Your doctor will review the medical history and symptoms and a physical examination will be performed. The following diagnostic tests may be ordered:
What are the Treatments for Renal Vascular Disease?
Treatment will depend on your symptoms, age, general health, and severity of the condition. It will also differ according to the type of renal vascular disease you have.
1
Renal Artery Stenosis
Blood pressure medication and cholesterol-lowering medications are prescribed for atherosclerosis in patients with renal artery stenosis. Endovascular procedures such as angioplasty, placement of a stent, and open surgery to bypass the blocked renal artery are examples of surgical treatments.
2
Renal Artery Thrombosis
Thrombolytic medication may be injected into the renal artery for several hours to several days to break up a blood clot. In some cases, surgery to remove the clot or bypass the artery may be required.
3
Renal Artery Aneurysm
Treatment of a renal artery aneurysm depends on symptoms and the size and location of the aneurysm. Smaller aneurysms may not need to be treated, but they should be monitored for growth or other issues. Aneurysms that are growing larger or expanding may require surgery.
4
Atheroembolic Renal Disease
Medicines to lower cholesterol, blood pressure, and treat other related conditions such as diabetes, may be used as part of the treatment. Lifestyle changes include diet, exercise, and avoiding fats and salty foods. Angioplasty or implantation of a stent and open surgery to bypass the blocked renal artery are surgical treatment options.
5
Renal Vein Thrombosis
Anticoagulants, which prevent blood from clotting, are commonly used to treat renal vein thrombosis. They may be given intravenously (IV) for a few days, then given orally for a few weeks or more.
Important Links
Practice Location
- © Dr. Neil Desai, Vascular Surgeon Cypress, Houston, TX

