Minimally Invasive Vascular Surgery
What is Minimally Invasive Vascular Surgery?
Vascular surgery refers to a variety of different surgical procedures performed to treat disorders of the arteries, veins, and lymph vessels of the body, excluding those in the heart and brain.
Open vascular surgery is a surgical technique in which large incisions are made on the area of the defect to repair or unblock arteries and veins using standard instruments. Minimally invasive vascular surgery is a surgical technique that is performed under general or local anesthesia and involves making smaller incisions to access the area of defect in the blood vessels and lymphatic system, without making larger incisions. Through these small incisions, tiny cameras and special instruments are used to magnify and project images of the veins and arteries onto a high-definition monitor and carry out the required repair more precisely.
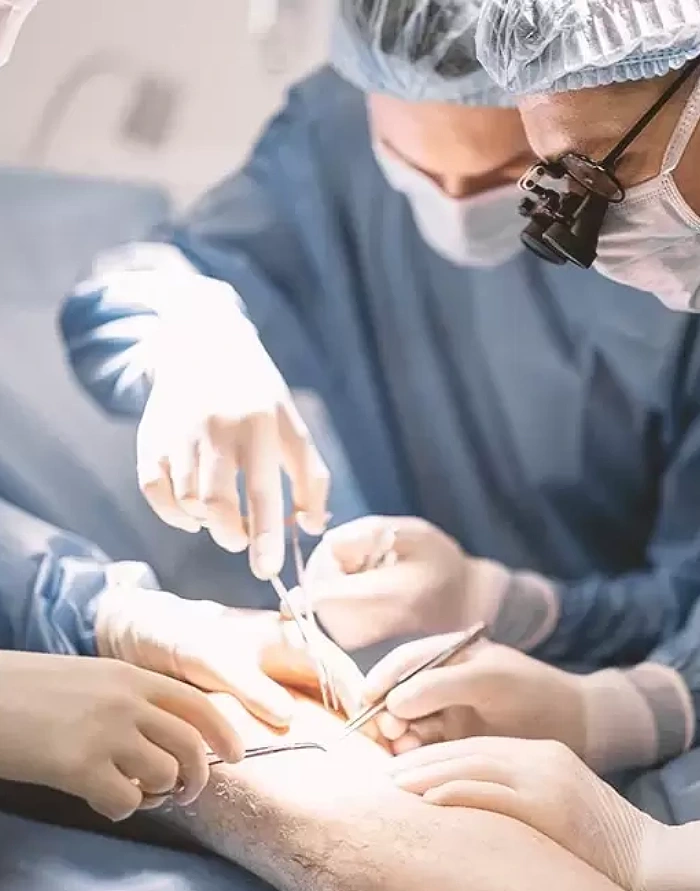
Indications for Minimally Invasive Vascular Surgery
Minimally invasive vascular surgery is usually recommended when non-surgical treatments have failed to treat the diseases involving the arteries and veins. It is often performed to improve blood circulation to an area of the body where the blood vessels have been damaged or the blood flow has been obstructed, following injury, disease, or other conditions. Some of the common vascular conditions that may warrant minimally invasive vascular surgery include:
Preparation for Minimally Invasive Vascular Surgery
Preoperative preparation for minimally invasive vascular surgery may involve the following steps:
- A thorough examination is performed by your doctor to check for any medical issues that need to be addressed prior to surgery.
- Depending on your medical history, social history, and age, you may need to undergo tests such as bloodwork and imaging to screen for any abnormalities that could compromise the safety of the procedure.
- You will be asked if you have allergies to medications, anesthesia, or latex.
- You should inform your doctor of any medications, vitamins, or supplements that you are taking.
- You may need to refrain from supplements or medications such as blood thinners or anti-inflammatories for a week or two prior to surgery.
- You should refrain from alcohol or tobacco at least a few days prior to surgery and several weeks after surgery.
- You should not consume solids or liquids at least 8 hours prior to surgery.
- A written consent will be obtained from you after the surgical procedure has been explained in detail.
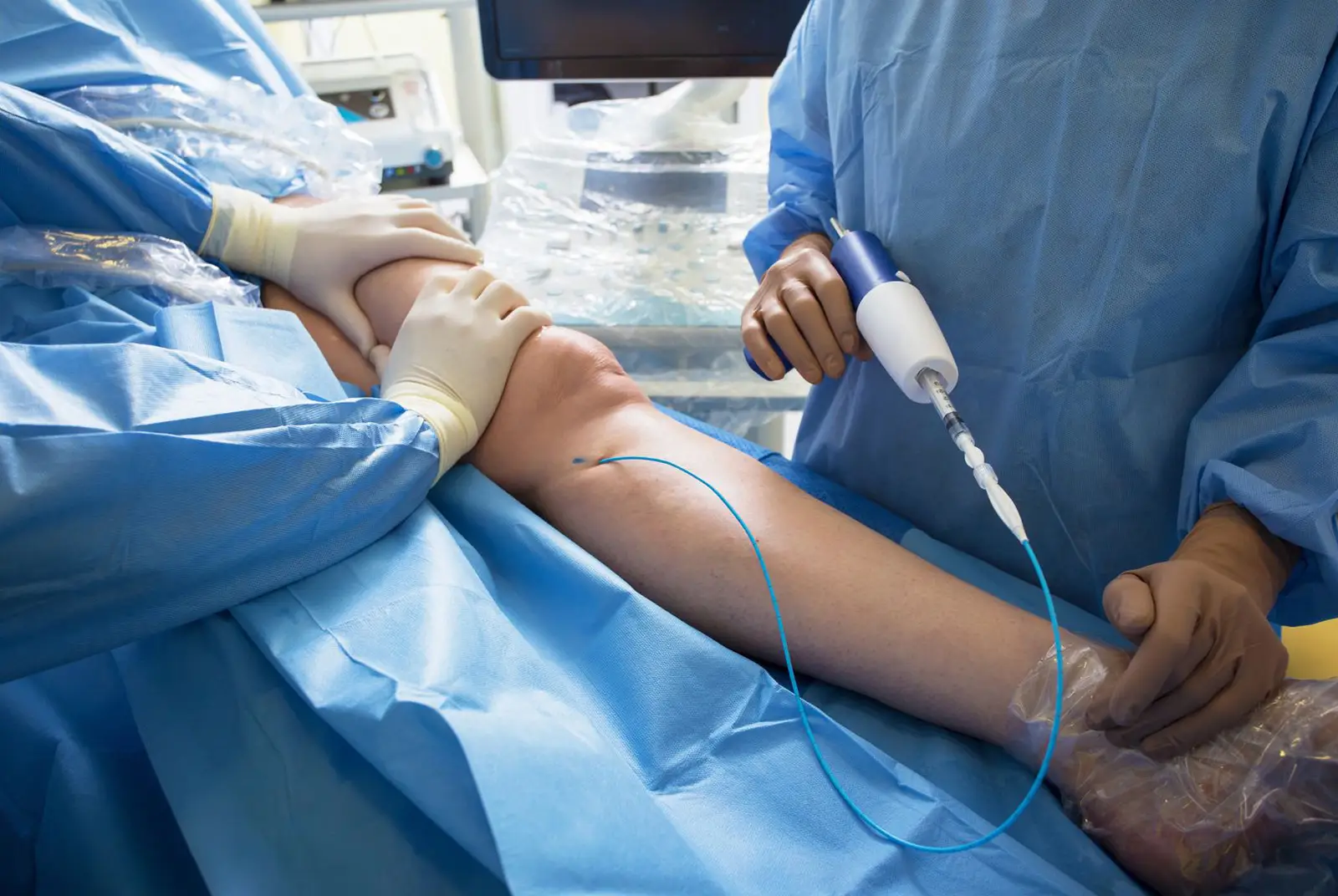
Common Minimally Invasive Vascular Surgeries
Some of the common minimally invasive vascular procedures include:
Post-Operative Care
Following the surgical procedure, you may experience pain or discomfort for which your surgeon will prescribe medications. You may be allowed to go home after 2 to 3 days. You can usually resume normal activities and return to work within 2 to 4 weeks after the surgery. Refrain from strenuous activities and lifting heavy weights for a defined period. Keep your surgical site clean and dry. Instructions on surgical site care and bathing will be provided. You will be advised to take your prescribed medications and make a few lifestyle changes such as quitting smoking, exercising regularly, maintaining a healthy weight, and eating a healthy diet. A periodic follow-up appointment will be scheduled to monitor your progress.
Benefits of Minimally Invasive Vascular Surgery
Minimally invasive vascular surgery provides various benefits including:
- Smaller scars
- Decreased risk of infection
- Less bleeding
- Reduced requirement of transfusion
- Less post-operative pain
- Fast recovery
- Shorter hospital stays
- Quicker return to daily normal activities
Risks and Complications
Minimally invasive vascular surgery is a relatively safe procedure; however, as with any surgery, some risks and complications may occur, such as the following:
1
Infection
2
Bleeding
3
Blood clots
4
Stroke
5
Heart attack
6
Allergic/anesthetic reactions
7
Damage to adjacent tissues or organs
Important Links
Practice Location
- © Dr. Neil Desai, Vascular Surgeon Cypress, Houston, TX

