Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
What is Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is a serious condition where a blood clot forms in one or more of the deep veins in your body. It most commonly happens in the lower leg or thigh but can also occur in other deep veins.
What are the Causes of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
DVT is caused by a blood clot—a clump of blood that turns solid. This clot blocks a vein, disrupting normal blood flow. Blood clots can form for several reasons, including:
- Damage to a vein from surgery or trauma
- Inflammation due to infection or injury
- Reduced mobility or long periods of inactivity (like sitting for hours)
- Certain medications that affect blood clotting
What are the Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
The signs and symptoms of deep vein thrombosis (DVT) can include:
- Swelling in the affected leg
- Pain or tenderness in the leg, often starting in the calf
- Red or discolored skin on the leg
- A feeling of warmth in the affected area
Risk factors of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Several factors can increase your risk of developing deep vein thrombosis (DVT), including:
- Age: Being over 60 years old.
- Prolonged inactivity: Sitting for long periods, like during long drives or flights.
- Injury or surgery: Trauma or recent surgical procedures.
- Pregnancy: Increased pressure on veins in the pelvis and legs.
- Obesity: Being overweight or obese.
- Smoking: Damages blood vessels and affects circulation.
- Heart failure: Increases the risk of blood clots.
- Inflammatory bowel disease: Conditions like Crohn’s disease or ulcerative colitis.
- Family history: A history of DVT or blood clots in close relatives.
- Genetics: Inherited conditions that affect blood clotting.
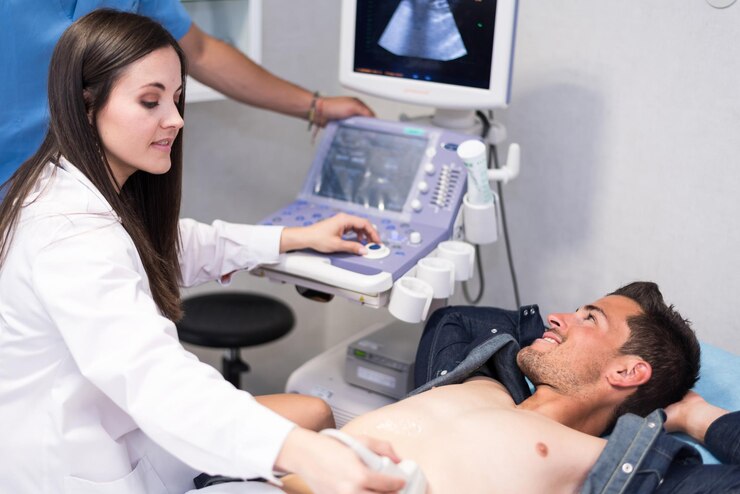
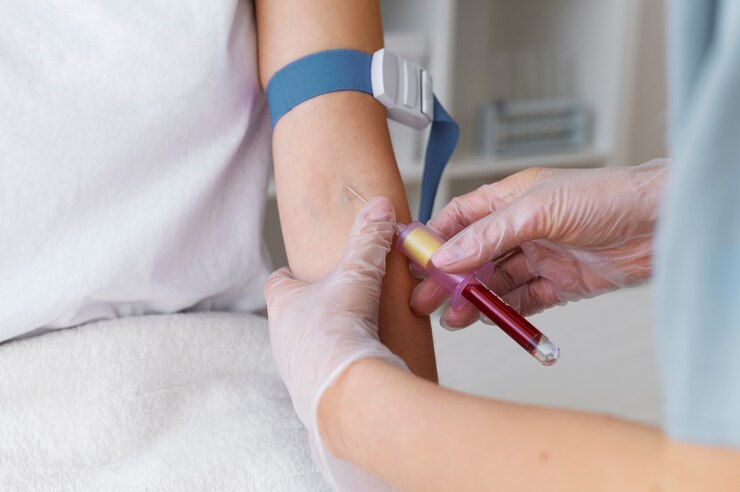
Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)
Your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms and based on this a physical examination is performed to check for areas of swelling, tenderness, or changes in skin color. Your doctor may also recommend the following diagnostic tests:
Blood clots produce D dimer, a type of protein. Almost all people with severe DVT have increased blood levels of D dimer. A normal D-dimer test result can often help rule out DVT.
Sound waves are used to create images of how blood flows through your veins in this noninvasive examination. It helps to identify a blood clot and evaluate blood flow through your arteries and veins.
This is a special x-ray examination in which a contrast substance is injected to visualize how blood flows through your veins.
An imaging study that uses a large magnetic field and radio waves to detect DVT in veins of the abdomen.
What are the Treatments for Deep Vein Thrombosis (DVT)?
Treatment options for deep vein thrombosis include:
Anticoagulants, often known as blood thinners, are the most common treatment for deep vein thrombosis. These therapies will not eliminate existing blood clots, but they can help keep them from growing larger and reduce your risk of getting more blood clots. Blood thinners can be taken orally, delivered intravenously, or injected under the skin.
If you have a more serious type of DVT or if other medications aren’t working, thrombolytic drugs may be recommended. These medications are administered through an IV or a tube (catheter) inserted directly into the clot. Clot busters are normally reserved for those who have major blood clots because they might cause serious bleeding.
If you are unable to use blood thinners, you may need a filter implanted in the vena cava, a big abdominal vein. A vena cava filter keeps clots from getting into your lungs when they break loose from the site of origin. A blood clot that travels to the lungs is called a pulmonary embolism and is a medical emergency.
These are special socks or stockings that support the walls of the blood vessels in the legs and help prevent blood from pooling and clotting. You will be instructed to wear them on your legs from your feet to around the level of your knees to help reduce swelling caused by deep vein thrombosis.
Surgery
If you have a deep vein thrombosis clot in your arm or leg, your doctor may recommend surgery to remove it. This is usually reserved for very large blood clots or clots that are causing major problems, such as tissue damage.
Prevention
Deep vein thrombosis can be prevented by taking the following steps
1
Avoid sitting still for long periods of time
2
Maintain a healthy weight
3
Get regular
exercise
4
Avoid
smoking
5
Drink plenty of fluids to avoid dehydration
Important Links
Practice Location
- © Dr. Neil Desai, Vascular Surgeon Cypress, Houston, TX

