Stereotactic Radiosurgery (SRS)
What is a Stereotactic Radiosurgery?
Stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) is a non-surgical procedure and a form of radiation therapy employed to treat lesions/tumors in the brain and spine. Stereotactic refers to locating a structure by means of three-dimensional coordinates. The SRS procedure involves using three-dimensional computerized imaging to locate and precisely deliver a high-concentrated dose of radiation to brain tumors or lesions in a single session with minimal impact on the surrounding healthy tissue.
Despite its name, stereotactic radiosurgery is not a surgery in the traditional sense as no incisions are made, and no general anesthesia is needed for adults. Stereotactic radiosurgery functions by distorting and destroying the DNA of the lesions/tumors in the brain, which results in these cells losing their ability to reproduce and die.
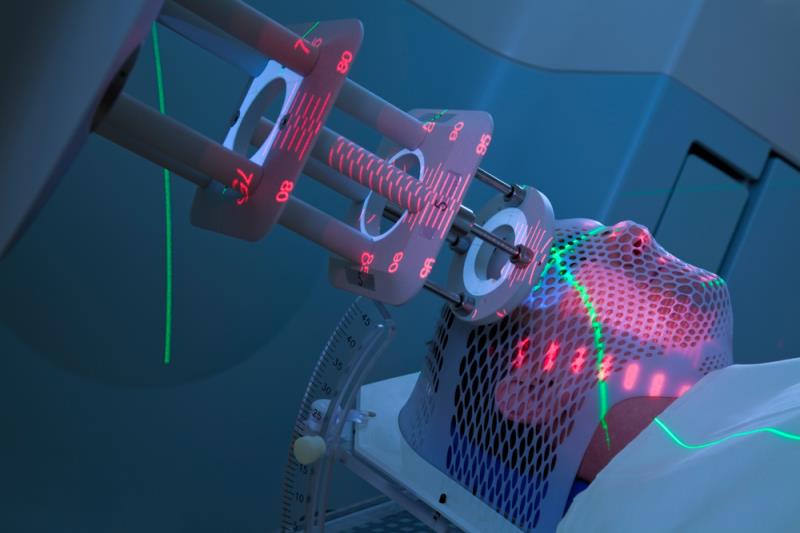
There are several types of stereotactic radiosurgery systems. However, the main types of SRS systems include:
Each system has unique features, but all achieve the same objective:
- Exactly locate the target (lesion or tumor)
- Hold the target still
- Direct the radiation beam towards the target
- Deliver a specific dose of radiation
Indications for Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Your surgeon may indicate stereotactic radiosurgery to treat conditions, such as:
- Pituitary tumors
- Tumors in the skull base
- Malignant gliomas
- Meningiomas
- Acoustic neuromas
- Metastasis of cancer to the head, brain, or neck area
- Arteriovenous malformation (AVM)
Preparation for Stereotactic Surgery
Pre-procedure preparation for stereotactic surgery will involve the following steps:
- A thorough physical examination is performed by your doctor to check for any medical issues that need to be addressed prior to surgery.
- Depending on your medical history, social history, and age, you may need to undergo tests such as blood work and imaging to help detect any abnormalities that could threaten the safety of the procedure.
- Your physician will discuss with you and recommend the radiation system that is best suited for your condition.
- You should inform your doctor of any medications, vitamins, or supplements that you are taking.
- Inform your doctor if you have any allergies to medications or dyes that may be used for the procedure.
- You should not consume any solids or liquids after midnight the day before your procedure.
- Wear comfortable and loose-fitting clothes and avoid wearing items such as jewelry, make-ups, and contact lenses during the procedure.
- Arrange for someone to drive you home as you will not be able to drive yourself after the procedure.
- A written consent will be obtained from you after the risks and benefits of the procedure has been explained in detail.
Procedure for Stereotactic Radiosurgery
Stereotactic radiosurgery may take about 30 minutes to an hour or longer based on complexity and the number of targets. In general, the procedure involves the following steps:
- A radiation oncologist and neurosurgeon are your primary caregivers and are accountable for the effective and safe administration of radiation and completion of the procedure.
- Based on the tumor’s location and size, either a LINAC face mask or a CyberKnife stereotactic head frame attached to your head using small pins will be used to hold your head firmly in position during the treatment.
- Next, you will undergo computer-guided three-dimensional imaging using MRI or CT scans while wearing the head frame or face mask.
- Information about the tumor’s dimension, size, location, and proximity to critical structures are gathered by the MRI or CT scan.
- Advanced computer software utilizes these scans to create a three-dimensional view of your anatomy and the tumor.
- The radiation machine is calibrated and prepared based on the obtained information and a treatment plan specific to your condition is formulated.
- You will be placed on the table with your head frame or face mask on and secured to the table to keep still.
- Alignment x-rays and lasers are used to position you correctly and stereoscopic x-rays are taken and compared to the formulated treatment plan to correct any misalignments before treatment is started.
- Once finalized, your therapist operates the machine from the control room and precisely directs the radiation beams through the skin to the target area from multiple directions to destroy the tumors.
- At the completion of the procedure, the face mask or head frame is removed, and the patient is discharged to the care of a family member.
Recovery
If a stereotactic head frame is used as part of the SRS procedure, then bandages are applied over the pin sites which should be removed the following day. You may experience swelling, pain, or tenderness from the pin sites; anti-inflammatory and pain medications are provided as needed to mitigate the discomfort. Most patients will be able to go home after the procedure following observation for a specified time to assess for any untoward reactions. Most patients will be able to return to their daily routines the following day if swelling or pain is not bothersome.
Benefits of Stereotactic Surgery
Some of the benefits of stereotactic surgery include:
- High-level of safety and precision during tumor destruction
- Leaves normal, healthy brain tissue relatively intact
- Ability to navigate precisely within the brain and eliminate tumor tissue
- Ability to reach deepest sections of the brain and destroy lesions not possible with conventional surgery
- Minimal risks and discomfort as it is a non-invasive procedure
- Quick recovery
- Short hospital stay for a few hours to a maximum of an overnight stay
Risks and Complications
Stereotactic radiosurgery is a relatively safe procedure; however, as with any procedure, some risks and complications may occur, such as:
1
Headaches
2
Fatigue
3
Brain swelling
4
Difficulty swallowing
5
Skin issues in the pin sites
6
Nausea and vomiting
7
Loss of hair in the treatment area
Important Links
Practice Location
- © Dr. Neil Desai, Vascular Surgeon Cypress, Houston, TX

